LONDON (Reuters) – Global markets are telling conflicting stories about the possible longer-term impact of U.S. tariffs on growth, a schism that investors say means either stocks or bonds could see a steep correction once it’s clear which is right.
U.S. President Donald Trump’s erratic approach to trade policy that generated so much volatility earlier this year seems to have left markets wary of reacting to his near-daily announcements on who, or what, might get hit with tariffs.
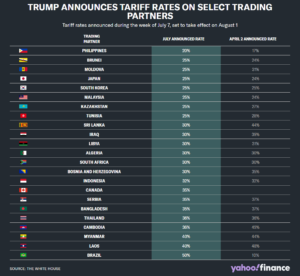
The latest target is Canada, which on Thursday Trump said will face a 35% duty, while most other trading partners will get blanket tariffs of 15% or 20%, eliciting barely a flutter in the broader markets. An announcement on Europe is imminent.
Investors say this apparent composure is less about confidence in an ultimately benign longer-term outlook, and more typical of a late-stage bull market, where the optimists scramble to catch the rally before it fizzles out, while the pessimists quietly prepare for trickier times ahead.
In one corner are riskier assets like stocks and cryptocurrencies. Shares on Wall Street have hit record highs, powered by enthusiasm around artificial intelligence and the prospect of a string of interest-rate cuts from the Federal Reserve as the economy gradually slows and the hit to inflation from tariffs proves mild so far. Bitcoin is near a record $112,000.
In the other corner are government bonds, gold and even crude oil, all of which are reflecting a belief that tariffs could derail the U.S. economy and growth everywhere will falter.
Premier Miton chief investment officer Neil Birrell said the second half of this year will be when the impact of Trump’s tariffs becomes obvious.
“It’s difficult for me to look at all this with any form of confidence or certainty,” he said, referring to the unpredictability of Trump’s policymaking and the possible impact of his “One Big Beautiful Bill”.
His main concern about stocks was U.S. households’ high participation in Wall Street, where a decline could quickly spread globally.
“Any stress in the U.S. economy that impacts the consumer and then impacts equity markets becomes a rather brutal and bloody downward spiral.”
Trump’s 90-day pause after April 2’s “Liberation Day” tariff announcement has been replaced by a scattergun application of levies on trading partners large and small, right ahead of the second-quarter earnings season which may yield the first clues about how severe the hit to corporate profits could be.
“Things have settled down but not in a positive way,” Amundi’s head of global macro Mahmood Pradhan said.
“The effective tariff rate for all imports coming into the U.S., if you calculated an average across the board, would be about 15%,” he said. “This is broadly negative for growth in every country that is involved in world trade.”
The World Bank last month cut its global growth forecast for 2025 by four-tenths of a percentage point to 2.3%, saying that higher tariffs and heightened uncertainty posed a “significant headwind” for nearly all economies.
With so much uncertainty hanging over U.S. assets, investors’ cash has flowed elsewhere for much of this year, into the likes of European stocks and bonds, gold, Chinese tech stocks or emerging market currencies.
Greasing the wheels of the stock market rally has been anticipation that Fed Chair Jerome Powell will cave to pressure from Trump to deliver a rapid string of rate cuts.
Yet the data has been too strong to justify an aggressive loosening of monetary policy and too soft to argue that tariffs are having no effect. U.S. employment figures show the economy is still creating jobs at a firm clip, while business activity surveys show factories and services are flagging.
In the meantime, Trump’s landmark tax cut and spending bill will add an extra $3.3 trillion to the national deficit.
Benchmark 10-year U.S. Treasury yields (^TNX) have retreated from January’s 15-month peaks at 4.8% to 4.35%.
“Bonds are much more focused on growth (falling) than on inflation so when you see an upturn in trade war announcements bond yields tilt towards lower growth and rate cuts. But equities are emboldened because tariffs haven’t shown up in the inflation numbers yet,” Joost van Leenders, senior investment strategist at Dutch asset manager Van Lanschot Kempen, said.
“We don’t think this can continue,” he said, adding he remains neutral on equities, with a small overweight position in government bonds.
Gold (GC=F) has staged a blistering 26% rally this year, topping $3,300 an ounce, serving as a hedge against macro and geopolitical uncertainty, as well as an alternative to the dollar, the biggest tariff casualty, which has lost over 10% in value this year against a basket of currencies.
Kevin Thozet, investment committee member at French asset manager Carmignac, said he is hedging against a fall in the U.S. stock market, but believes this is unlikely right now because retail traders are diving in to buy market dips.
Further out, he said Trump’s tax cut bill might offset some of the impact of tariffs, but the extra debt it could take to fund those cuts could drive the 10-year Treasury yield to 5% in the coming three months, a level that policymakers worry about given its impact on households, companies and the government.
“We see significant cracks in U.S. markets, even though the Fed has ample room to cut,” he said.
(Reporting by Amanda Cooper and Naomi Rovnick; Editing by Elaine Hardcastle)
Shared by Golden State Mint on GoldenStateMint.com














